
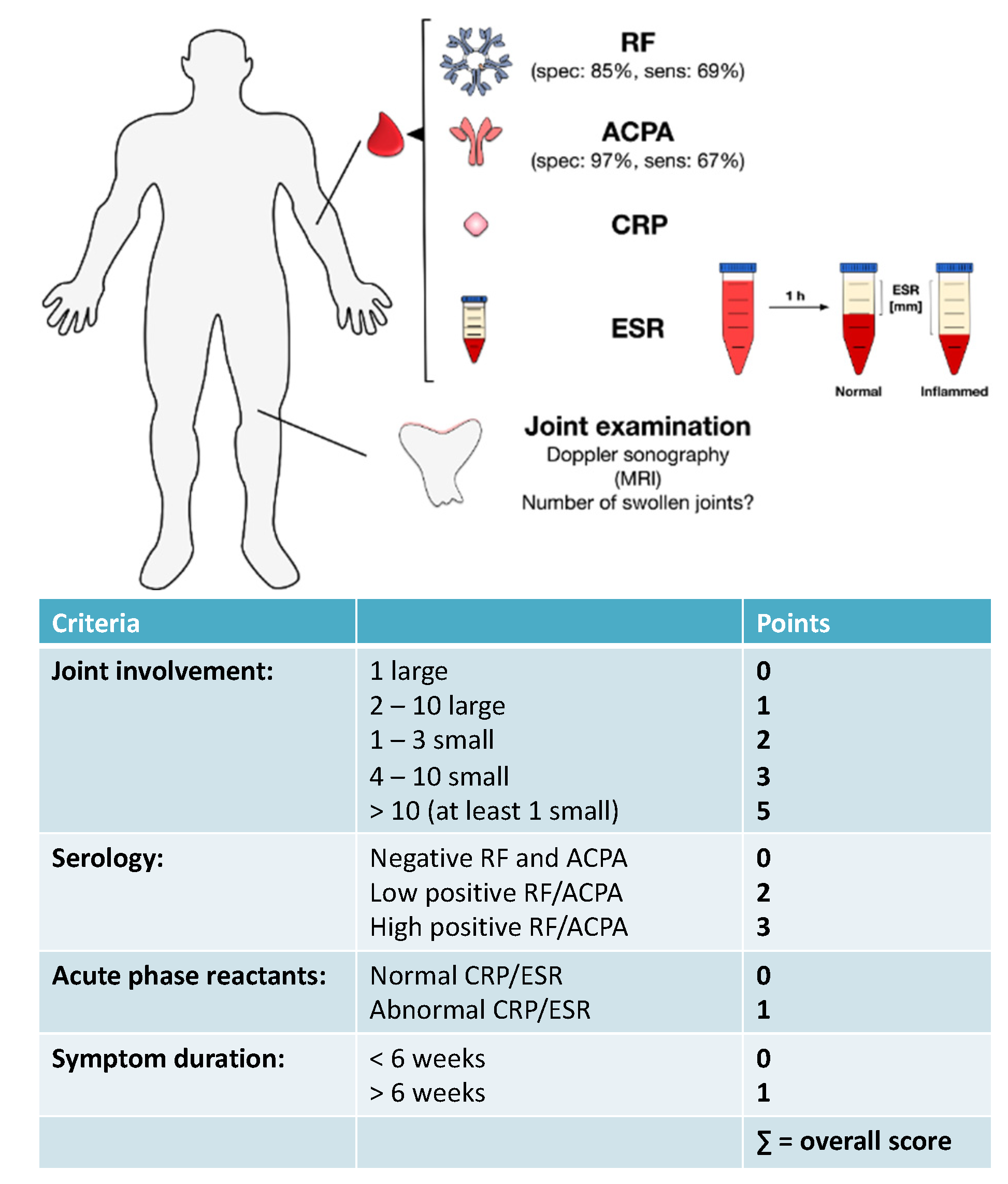

Rheumatoid arthritis was historically categorized based on the American Rheumatism Association Functional Class and Anatomic Stage, both proposed by Dr. These antibodies occur in approximately 70-80% of patients and are important for diagnosis and early recognition. Anti-CCP (cyclic citrullinated peptide) antibodies are directed to proteins that have a modified amino acid called citrulline. The patient with RA characteristically produces autoantibodies called rheumatoid factors and anti-CCP. In RA, inflammation of the joint can lead to erosion or damage of cartilage and bone and eventual deformity. As a systemic disease, RA is associated with symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, and depression. It can take months before a patient seeks medical attention, usually when joint pain (arthralgia) progresses to swelling and tenderness of the joint. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition and, while it may occur acutely in some patients, onset is usually gradual. Over time, RA can affect other organs (eg, eyes, lungs) and can lead to increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
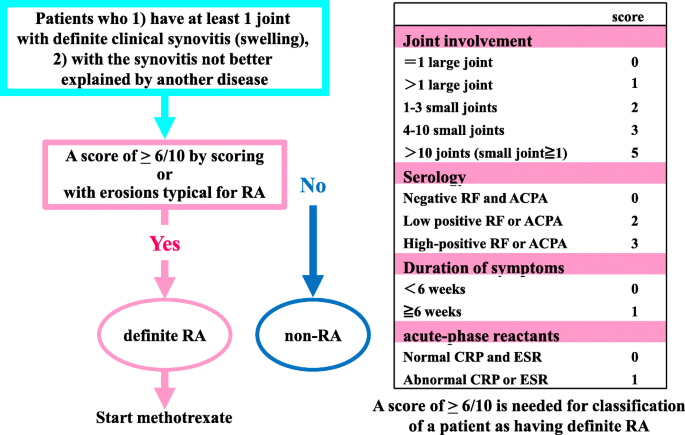
Rheumatoid arthritis is a form of polyarthritis and involves many joints, both large and small it can also affect the cervical spine. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease that produces inflammatory arthritis (stiff, painful, swollen joints, usually symmetrical).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
